As night falls over Australia’s forests, grasslands and backyards, the hidden world of nocturnal insects stirs to life. In many ecosystems, overall insect activity actually peaks at night, especially in warmer regions of the world.
These nighttime creatures play essential roles in ecosystems, providing services such as pollination, waste decomposition, and pest control. Here are some of the remarkable insects that come out after dark – and why they matter.
Tanya Latty
Moths: the stars of the night shift
While their flashier daytime relatives, the butterflies, often steal the spotlight, moths are the hidden stars of the night shift.
An estimated 22,000 species of moth call Australia home, and most are nocturnal, although some are diurnal (day active) or crepuscular (active at dawn and dusk).
Many species feed on flower nectar using their long, straw-like mouthparts, transferring pollen between flowers as they go.
In the Snowy Mountains, for instance, scientists found moths carry pollen from 19 different plant species.
While some moths feed on a wide variety of plants, others have evolved highly specialised relationships with specific flowers.
For instance, more than 500 species of leaf flower trees (Phyllanthus) across tropical Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Pacific are dependent on tiny leaf flower moths (Epicephala) for their pollination.
The trees’ flowers attract moths by producing nectar at night, when the moths are most active.
The larvae of moths, caterpillars, also play a vital role in ecosystems. For example, the larvae of Mallee moths (Oecophoridae) feed on dry leaves in the leaf litter, making them essential for the decomposition of tough, dry plant material.
Without their tireless work breaking down organic matter, leaf litter can accumulate to problematic levels.
Although most caterpillars feed on plant material, some have unusual diets. Trisyntopa neossophila caterpillars, for example, feeds on the faeces of parrots nesting in termite mounds.
Some caterpillars are even predators. The larvae of the brown scale moth (Mataeomera coccophaga), for instance, eats scale insects.
Moths and their larvae provide a fat and protein-rich food source for many animals, including humans.
Once so abundant they famously blanketed the 2000 Sydney Olympics, large bogong swarms have become increasingly rare, putting at risk species that depend on them for essential nutrients.
Busy night beetles
Seeing the tiny, flashing lights of fireflies dancing through the darkness on a summer night is a magical experience.
Fireflies are actually beetles in the family Lampyridae, and 25 species call Australia home.
Each firefly species uses its own distinctive flash pattern to communicate with potential mates.
When large numbers of the same species gather, they can synchronise their light pulses, creating a breathtaking light show.
The fireflies’ distinctive light is produced through a biochemical reaction involving a molecule called luciferin and an enzyme called luciferase. When these interact in the presence of oxygen, they emit light.
Adult fireflies do not eat but firefly larvae mostly eat snails, which helps keep snail populations under control.

Tanya Latty
Beetles in the scarab family are often active at night. Large numbers of Christmas beetles (Anoplognathus spp) flying around porch lights used to be a common sight, but numbers appear to be in decline.
Some native dung beetles, such as the five-horned dung beetle (Onthophagus pentacanthus), are also nocturnal. Hardworking dung beetles play a vital role by breaking down animal dung, helping to recycle nutrients and improve soil health.
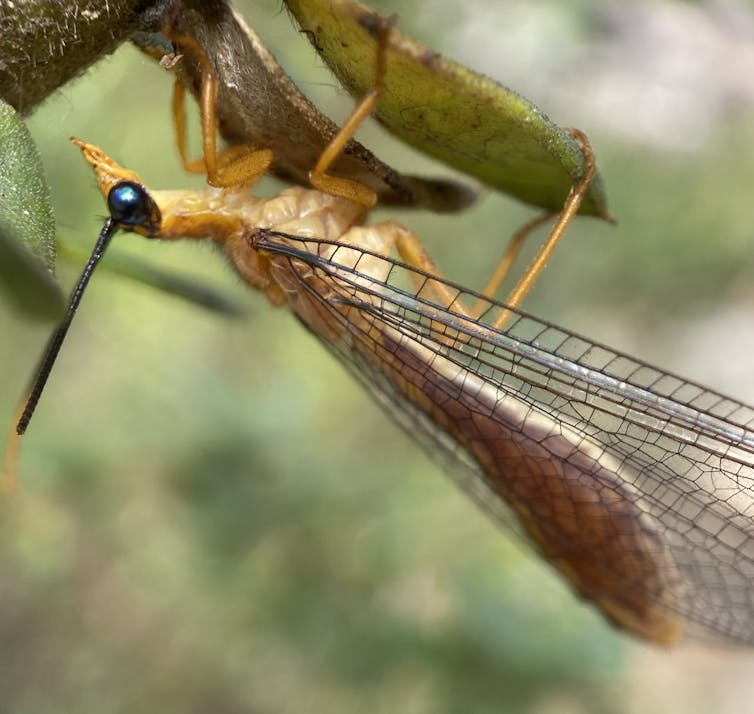
Lacewings and mantisflies
Lacewings belong to an ancient group of insects (Neuroptera) named for the delicate, lace-like net pattern of veins on their wings.

Tanya Latty
Most adult lacewings are nocturnal predators, feeding on smaller insects using their hollow, scissor-shaped mouthparts to catch and suck the nutrients from their prey.

Tanya Latty
Several lacewing species are effective pest controllers and are used in agriculture to manage pests such as aphids and mealybugs.
Mantid lacewings, also known as mantisflies, resemble a strange hybrid between a mantis and a fly but are actually in the same group as lacewings.
The larvae of mantisflies are poorly studied, but most species are believed to be predators of insects, although some are predators of spider eggs. By eating other insects, mantisflies may play a role in controlling pest populations.
Protecting these night shift workers
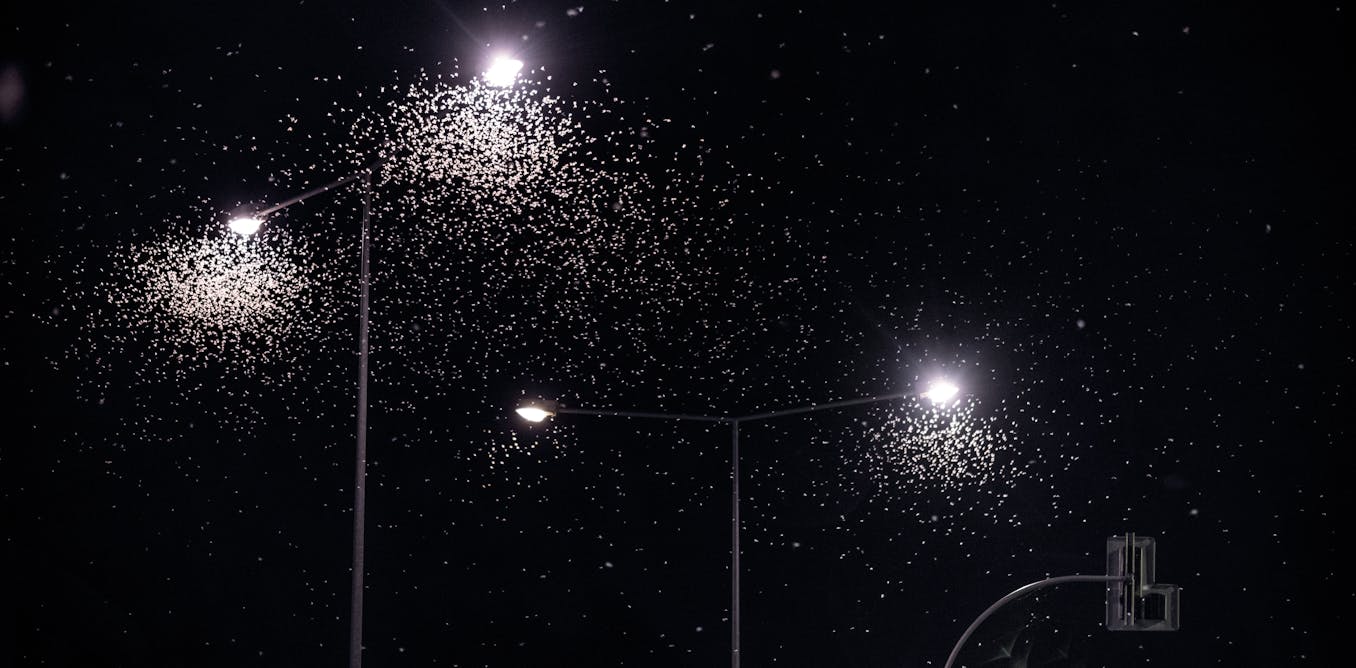
Artificial lights at night are causing serious disruption to insects on the night shift.
Insects often become disoriented, flying in endless circles around bright lights, burning energy they cannot afford to lose. This confusion can lead to exhaustion or death.

Tanya Latty
Artificial lighting at night can also disrupt nocturnal insect reproduction. And, predators such as owls and bats may learn to hunt around artificial lights where prey becomes more concentrated and vulnerable.
The exact reasons why nocturnal insects are drawn to light remain unclear, but recent research suggests that some nocturnal insects use light to maintain stable, level flight by orienting their bodies so light hits their upper surface.
This system works well when the only lights present at night are the Moon and stars, but fails when artificial lights disrupt the night.
We can help protect nocturnal insects by:
- turning off unnecessary outdoor lights at night, especially during summer when many insects are breeding
- using motion-activated lights to reduce light pollution
- reducing or eliminating the use of insecticides in our gardens.
Small changes can make a big difference to help protect the insects working hard overnight to keep our ecosystems healthy.

The post “While you sleep, these insects are working hard on the night shift to keep our environment healthy” by Tanya Latty, Associate Professor, School of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Sydney was published on 01/31/2025 by theconversation.com


































Leave a Reply