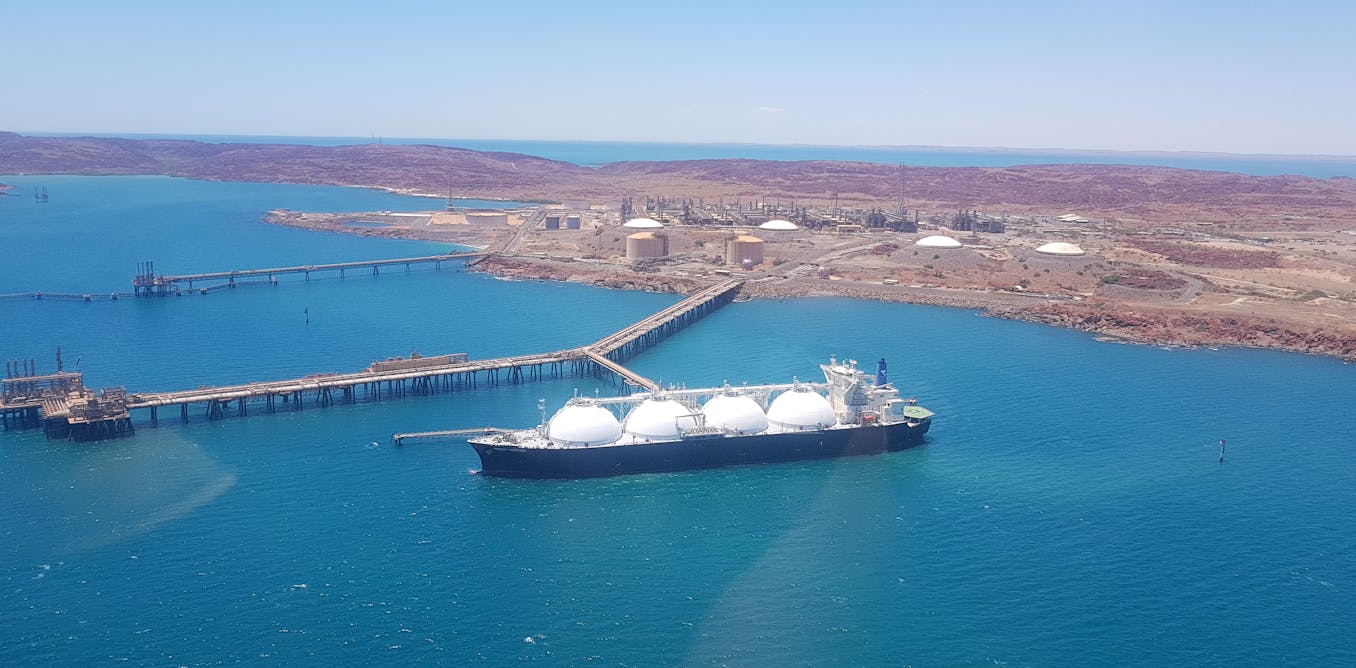
In a decision surprising very few people, Australia’s new environment minister Murray Watt has signed off on an extension for the gas plant at Karratha, part of the enormous North West Shelf liquefied natural gas project.
The decision had been deferred until after the federal election, given significant environmental concerns around the project.
This approval means the gas plant at Karratha can now keep running until 2070. The Woodside-operated project has helped to shape Australia’s reputation as one of the biggest suppliers of LNG in the world.
Watt did not have to consider climate impacts, but rather what damage the extension might do to ancient rock art as well as economic and social matters. His approval is “subject to strict conditions”, which largely focus on air emissions from the project. Critics claim the extension will threaten irreplaceable 50,000 year old rock carvings and petroglyphs.
The decision will enrage environmentalists. If the project continues to operate, it has been estimated to generate four billion tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions over 50 years.
Australia has committed to reach net zero emissions by 2050. But the majority of the gas extracted from the North West Shelf will be exported, meaning the huge emissions generated from its extraction, liquefaction, transportation and burning will not be counted domestically.
But while the Karratha plant now has a lifeline, there’s still an open question about where the gas will come from. For decades, the plant has processed gas from the North Rankin, Perseus and Goodwyn gasfields offshore. These are now running out.
The main purpose of extending the Karratha plant’s lifespan would be to process gas extracted from giant new gasfields lying underneath the pristine Scott Reef. Approval to open these gasfields has not yet been given because of the significant concerns extraction will damage the reefs.
Save our Songlines/AAP
What is the North West Shelf Project?
The North West Shelf development has been operational since the 1980s. Gas is extracted from huge basins located off the Pilbara coast and processed at the Karratha plant on the Burrup Peninsula.
To date, only a third of the 33 trillion cubic feet of gas in this basin has been extracted.
Woodside Petroleum is the project operator, holding a one-third shareholding along with Chevron and Shell in what is known as the North West Shelf Joint Venture.
The project is the largest producer of domestic gas in Western Australia, providing almost two-thirds of the state’s consumption. In the 2023-2024 financial year, it produced gas worth about A$70 billion.
Domestic consumers are paying much more for this gas than their international counterparts. For example, a $25 billion contract entered into with China in 2002 includes a guarantee prices will remain the same until 2031.
With the rapid escalation of gas prices, this means China is paying a third of the price paid by domestic consumers. Other markets for the gas include Japan and South Korea, which lack domestic gas resources.

Hans Wismeijer/Shutterstock
The ‘transition fuel’ worse than coal
Gas has long been touted as a transition fuel in a decarbonising economy. But this is questionable on several fronts.
Rather than replacing coal, LNG may actually be displacing renewables.
Worse, a recent study showed emissions from LNG are 33% higher than coal over a 20 year period when extraction, piping to a processing facility, compression, shipping, decompression and burning for energy are considered. “Ending the use of LNG should be a global priority,” the report concludes.
Turning methane-heavy natural gas into a liquid to allow it to be shipped overseas is energy intensive. Large leaks of methane from wells and pipes are common during extraction and transport. When the gas is finally burned to generate energy, it produces carbon dioxide.
In China, coal’s share of electricity production has been eroded by renewables but not by LNG, according to the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis.
From a big picture point of view, climate commitments can’t be met if high-emitting infrastructure keeps being commissioned. Alongside stopping the expansion of fossil fuel projects, existing fossil fuel infrastructure must be retired or retrofitted with cleaner technology.
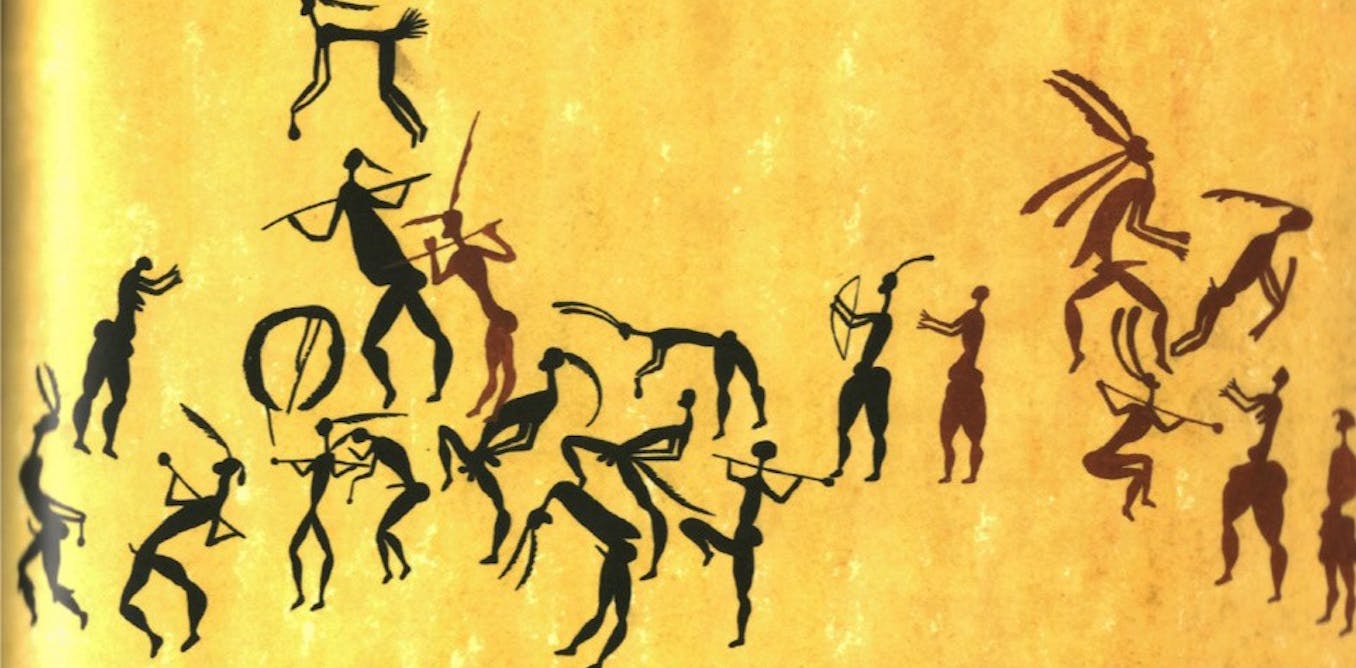
Eroding ancient rock art
The project’s processing plant is located on the Burrup Peninsula, also known as Murujaga. But this peninsula also has about 500,000 rock carvings by First Nations groups, the densest concentration in the world. In 2023, former environment minister Tanya Plibersek announced a bid to give this area World Heritage listing.
In a new draft decision, the United Nations World Heritage Committee flagged concerns over the bid and referred it back to the Australian government to “ensure the total removal of degrading acidic emissions” and “prevent any further industrial development” near the petroglyphs.
Gas production and ancient rock art are poorly matched. Research suggests processing plant gases such as nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and ammonia have been gradually eroding the fragile petroglyphs for decades. Successive state and federal governments have failed to act to safeguard this area.
Gas projects seem untouchable
Approving the North West Shelf extension is a disaster for the environment, our climate commitments and the fragile and irreplaceable rock art in Murujuga.
It would seem that despite well-founded concerns on many fronts, big gas projects in Australia are all but untouchable.

The post “North West Shelf gas plant cleared to run until 2070” by Samantha Hepburn, Professor, Deakin Law School, Deakin University was published on 05/28/2025 by theconversation.com




































Leave a Reply